-
Deisiú Fashion Showcase Celebrates Bioinspired Design and Sustainable PracticesDeisiú Fashion Showcase Celebrates Bioinspired Design and Sustainable PracticesDecember 2, 2024
-
 New Water PhD Platform Kicks Off Annual Meeting in Ben Guerir, MoroccoNew Water PhD Platform Kicks Off Annual Meeting in Ben Guerir, MoroccoNovember 25, 2024
New Water PhD Platform Kicks Off Annual Meeting in Ben Guerir, MoroccoNew Water PhD Platform Kicks Off Annual Meeting in Ben Guerir, MoroccoNovember 25, 2024 -
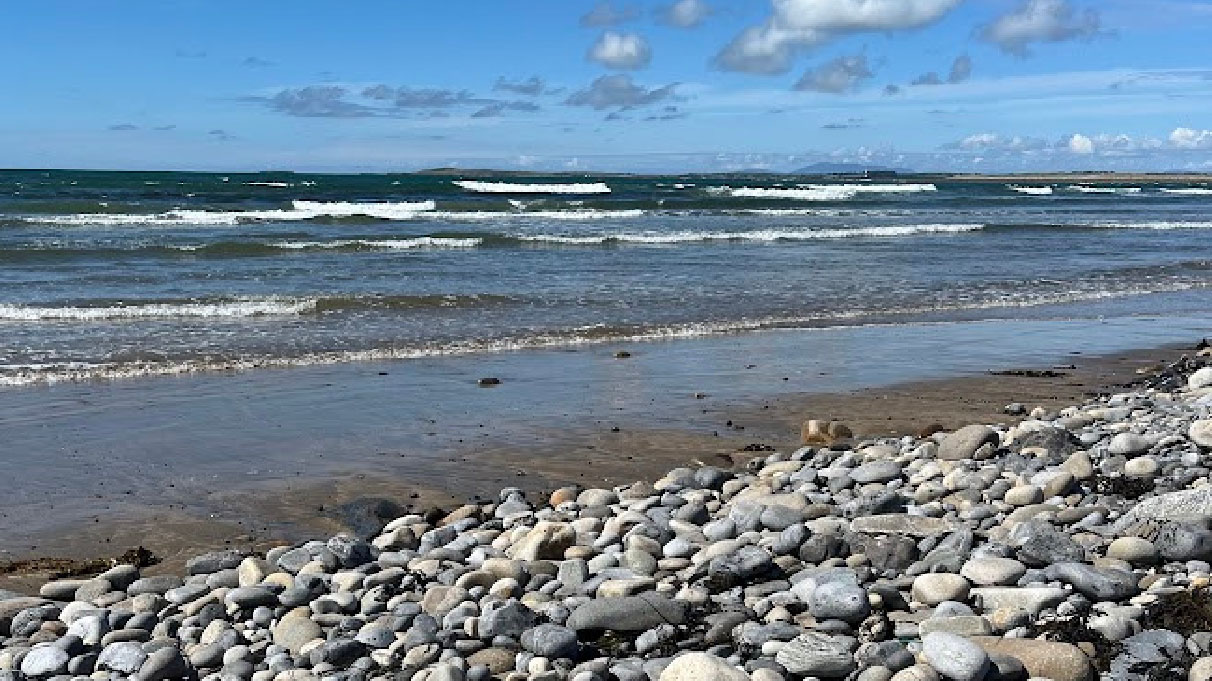 Look Back at 2024 DCU Water Institute Marine Research ActivityLook Back at 2024 DCU Water Institute Marine Research ActivityNovember 20, 2024
Look Back at 2024 DCU Water Institute Marine Research ActivityLook Back at 2024 DCU Water Institute Marine Research ActivityNovember 20, 2024 -

-
 Uisce Éireann Wins Top Prize at Water-Share Ireland Inaugural Hackathon at DCUUisce Éireann Wins Top Prize at Water-Share Ireland Inaugural Hackathon at DCUOctober 2, 2024
Uisce Éireann Wins Top Prize at Water-Share Ireland Inaugural Hackathon at DCUUisce Éireann Wins Top Prize at Water-Share Ireland Inaugural Hackathon at DCUOctober 2, 2024 -
 DCU WI uses biomimicry to develop coating to protect ships and equipmentDCU WI uses biomimicry to develop coating to protect ships and equipmentJanuary 8, 2024
DCU WI uses biomimicry to develop coating to protect ships and equipmentDCU WI uses biomimicry to develop coating to protect ships and equipmentJanuary 8, 2024 -
 Resounding Success: Waves of Change Conference by DCU Water Institute & Invent Receives Rave Reviews from AttendeesResounding Success: Waves of Change Conference by DCU Water Institute & Invent Receives Rave Reviews from AttendeesNovember 19, 2023
Resounding Success: Waves of Change Conference by DCU Water Institute & Invent Receives Rave Reviews from AttendeesResounding Success: Waves of Change Conference by DCU Water Institute & Invent Receives Rave Reviews from AttendeesNovember 19, 2023 -
 Conference: Waves of Change: Innovative Solutions for a Water-Wise World - open for registrationConference: Waves of Change: Innovative Solutions for a Water-Wise World - open for registrationOctober 20, 2023
Conference: Waves of Change: Innovative Solutions for a Water-Wise World - open for registrationConference: Waves of Change: Innovative Solutions for a Water-Wise World - open for registrationOctober 20, 2023

nurture talent to carry out multi and
transdisciplinary research, and generate
innovative solutions to global water challenges.

for innovations in water research
and education.
Latest Water Blog
-
 Highest Rate of Wildfires Grip Europe and The United KingdomHighest Rate of Wildfires Grip Europe and The United KingdomJuly 29, 2022
Highest Rate of Wildfires Grip Europe and The United KingdomHighest Rate of Wildfires Grip Europe and The United KingdomJuly 29, 2022 -

-

-

-

-
-

-

Latest Tweets
🦪🍤Shellfish are rich in healthy fats and minerals and when eaten regularly, may boost immunity, and promote brain and heart health
#10thingstoknowabout #feedingthefuture
Mussels are excellent sources of protein and, by weight, contain more iron than lean steak
#10thingstoknowabout #feedingthefuture
Over 30% of food is lost or wasted each year, so transforming food waste could help meet the growing global demand for feed protein
#10thingstoknowabout #feedingthefuture
Water, A Resource Less Valued
Water is the most precious commodity in the world, but it is not the most valued.
Click Here to Learn More-
 Research and InnovationResearch and Innovation
Research and InnovationResearch and Innovation -
 EventsEvents
EventsEvents
